摘要
上一篇在VS中创建了一个dll项目和一个C++客户端项目用来测试dll的功能。在本篇中会在dll中调用第三方库。其实在C++的控制台项目中和在dll项目中调用并没有太大的区别,都可以参考本文。
C++三方库介绍
俗话说的好,“不重复造轮子”,C++的生态虽然没有python方便,但还是有不少库能够提高开发效率的。除了可以直接调用的C++标准库外,还有比较出名的比如Boost、OpenCV等比较常用的库。
一般来说三方库可以分为两种,一种是提供了源码/编译好的源码,另一种是head-only的库。C++程序员会比较喜欢headonly的,因为可以直接#include,非常方便。这里我们展示两个库的使用,一个是spdlog,一个是FFTW,其他库的原理都是差不多的,学会之后就可以自行处理。
spdlog
spdlog是一个快速、异步的日志库,仓库地址 https://github.com/gabime/spdlog 。
下载好源代码,然后将include目录下的spdlog文件夹拷贝到我们解决方案目录下,新建一个目录取名为thridarty,专门用来放第三方库的代码。右击dll项目选择“配置属性”>“C/C++”>“常规”将thridarty添加到附加包含目录中
直接引用会报错,static_assert failed: 'Unicode support requires
compiling with
/utf-8',需要在属性页的“C/C++”>“命令行”中填写“/utf-8”可以实现配置,参考文档
可以编写下面的直接开始使用spdlog(默认输出在控制台)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 #include "spdlog/spdlog.h" spdlog::trace ("这是一条 trace 级别的日志(最详细)" ); spdlog::debug ("这是一条 debug 级别的日志" ); spdlog::info ("这是一条 info 级别的日志" ); spdlog::warn ("这是一条 warn 级别的日志" ); spdlog::error ("这是一条 error 级别的日志" ); spdlog::critical ("这是一条 critical 级别的日志(最严重)" );
spdlog使用方法
这里顺带介绍一下spdlog库的使用参考本文 。如果不需要可以跳过这部分,如果想直接嵌入工程,可以拷贝下一节的代码。
spdlog 的架构设计清晰,主要包含三个核心组件。
Formatter(格式化器)
Formatter
负责控制日志的输出格式,决定了每条日志包含哪些信息以及如何展示。spdlog
提供了合理的默认格式,包含日期时间、日志器名称、日志级别和日志内容。通过
set_pattern 方法可以自定义格式。
1 2 3 4 spdlog::set_pattern ("[%H:%M:%S %z] [thread %t] %v" ); some_logger->set_pattern (">>> %H:%M:%S %v <<<" );
Sink(通道)
Sink 是日志的输出目的地,每个 sink 都关联着一个
formatter,负责将格式化后的日志输出到指定位置。指定位置可以是控制台,也可以是文件
控制台:输出到命令行终端,支持彩色显示,_mt
后缀表示多线程安全版本:
1 auto console_sink = std::make_shared <spdlog::sinks::stdout_color_sink_mt>();
基础文件 1 auto basic_file_sink = std::make_shared <spdlog::sinks::basic_file_sink_mt>("log.txt" );
每日轮转的Sink 1 2 auto daily_sink = std::make_shared <spdlog::sinks::daily_file_sink_mt>("log" , 14 , 22 );
大小轮转的Sink 1 2 auto rotating_sink = std::make_shared <spdlog::sinks::rotating_file_sink_mt>("log" , 10 *1024 *1024 , 100 );
在写入文件的时候为避免日志缓存导致输出延迟,建议设置刷新策略
1 2 3 4 spdlog::flush_every (std::chrono::seconds (1 )); spdlog::flush_on (spdlog::level::debug);
Logger(日志器)
Logger 是日志操作的入口,每个日志器包含一个或多个
sink,日志信息会通过所有关联的 sink 输出。
默认日志器:spdlog
提供全局默认日志器,输出到控制台,多线程安全且支持彩色显示。 直接使用
1 spdlog::info ("这是默认日志器输出的信息" );
自定义日志器:可根据需求创建特定功能的日志器,有两种创建方式:
直接创建:适用于单个 sink 的场景 1 2 3 4 auto console_logger = spdlog::stdout_color_mt ("console_logger" );auto file_logger = spdlog::rotating_logger_mt ("file_logger" , "log.txt" , 10 *1024 *1024 , 100 );
组合 sink 创建:适用于多个 sink 的场景 1 2 3 4 5 6 std::vector<spdlog::sink_ptr> sinks; sinks.push_back (std::make_shared <spdlog::sinks::stdout_color_sink_mt>()); sinks.push_back (std::make_shared <spdlog::sinks::rotating_file_sink_mt>("log.txt" , 10 *1024 *1024 , 100 )); auto combined_logger = std::make_shared <spdlog::logger>("combined_logger" , sinks.begin (), sinks.end ());spdlog::register_logger (combined_logger);
日志和sink都可以设置日志级别,只有达到指定级别的日志才会被输出,级别从低到高排列为
trace -> debug -> info -> warn -> error -> critical。
1 2 3 4 combined_logger->set_level (spdlog::level::debug); sinks[0 ]->set_level (spdlog::level::info);
将spdlog嵌入dll项目
这里新建一个logger.h和logger.cpp文件将spdlog封装起来,在dll项目里新建两个文件,将下面的代码进行复制
logger.h文件 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 #pragma once #include <string> #include "spdlog/spdlog.h" #include "spdlog/sinks/daily_file_sink.h" class Logger { public : static bool Init (const std::string& log_dir, const std::string& log_name, int hour = 0 , int minute = 0 ) static std::shared_ptr<spdlog::logger> GetLogger () Logger (const Logger&) = delete ; Logger& operator =(const Logger&) = delete ; private : Logger () = default ; ~Logger () = default ; static std::shared_ptr<spdlog::logger> s_logger; }; #define LOG_TRACE(...) ::Logger::GetLogger()->trace(__VA_ARGS__) #define LOG_DEBUG(...) ::Logger::GetLogger()->debug(__VA_ARGS__) #define LOG_INFO(...) ::Logger::GetLogger()->info(__VA_ARGS__) #define LOG_WARN(...) ::Logger::GetLogger()->warn(__VA_ARGS__) #define LOG_ERROR(...) ::Logger::GetLogger()->error (__VA_ARGS__) #define LOG_CRITICAL(...) ::Logger::GetLogger()->critical(__VA_ARGS__)
logger.cpp
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 #include "logger.h" #include <filesystem> #include <iostream> namespace fs = std::filesystem;std::shared_ptr<spdlog::logger> Logger::s_logger = nullptr ; bool Logger::Init (const std::string& log_dir, const std::string& log_name, int hour, int minute) try { if (!fs::exists (log_dir)) { fs::create_directories (fs::path (log_dir)); } std::string log_file = log_dir + "/" + log_name; s_logger = spdlog::daily_logger_mt ("logger" , log_file, hour, minute); s_logger->set_level (spdlog::level::trace); s_logger->flush_on (spdlog::level::err); spdlog::flush_every (std::chrono::seconds (3 )); spdlog::set_default_logger (s_logger); return true ; } catch (const std::exception& e) { std::cerr << "Logger initialization failed: " << e.what () << std::endl; return false ; } } std::shared_ptr<spdlog::logger> Logger::GetLogger () if (!s_logger) { throw std::runtime_error ("Logger not initialized. Call Init() first." ); } return s_logger; }
修改dllmain.cpp的代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 #include <windows.h> #include "include/logger.h" BOOL APIENTRY DllMain ( HMODULE hModule, DWORD ul_reason_for_call, LPVOID lpReserved ) switch (ul_reason_for_call) { case DLL_PROCESS_ATTACH: Logger::Init ("./logs" ,"dll_log" , 2 , 0 ); LOG_INFO ("DLL loaded successfully" ); break ; case DLL_THREAD_ATTACH: LOG_DEBUG ("New thread attached" ); break ; case DLL_THREAD_DETACH: LOG_DEBUG ("Thread detached" ); break ; case DLL_PROCESS_DETACH: LOG_INFO ("DLL unloaded" ); spdlog::shutdown (); break ; } return TRUE; }
在MathLibaray.cpp的init这里添加测试函数(需要引用#include
"logger.h")
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 void fibonacci_init ( const unsigned long long a, const unsigned long long b) index_ = 0 ; current_ = a; previous_ = b; LOG_TRACE ("Entering DoSomething()" ); LOG_DEBUG ("Performing some operation" ); LOG_INFO ("DoSomething() executed successfully" ); }
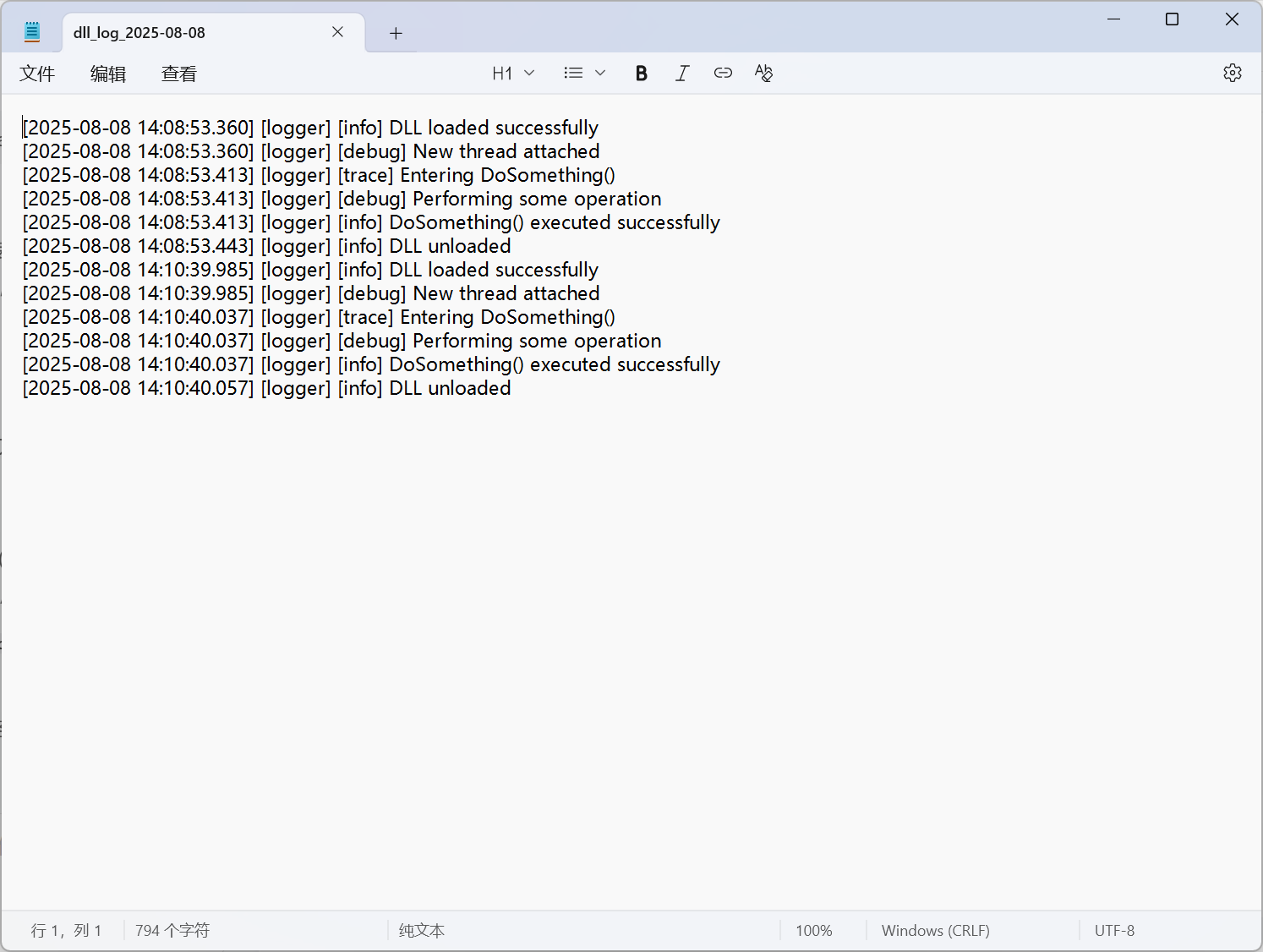
在测试台端,可以注释掉一半的代码,重新生成dll,并运行测试代码,会在测试客户端工程下面生成一个logs文件,里面会有一个写有当前日期的文件
logs文件
我这里运行了两次,所以有两块文本。
FFTW
FFTW(Fastest Fourier Transform in the
West)是一个高效的开源计算库,专门用于快速傅里叶变换(FFT)及其相关操作。FFTW不是一个headonly的库,它需要用户使用dll或者自己集成,不过FFTW提供了编译好的版本可以直接下载http://www.fftw.org/download.html
这里我们使用Windows64位版本的。
编译好的版本有dll和h文件,我们需要再编译出一个lib文件用于在Visual
Studio中静态链接,需要用vs提供的lib.exe工具。
打开VS的"x64 Native Tools Command Prompt for VS
2022"工具,用该工具进入到解压的文件夹下,运行指令
1 lib /machine:x64 /def:libfftw3-3.def
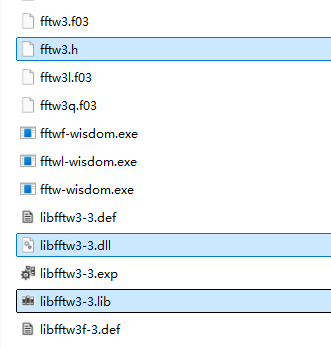
取出这三个文件- "fftw3.h" "libfftw3-3.dll" "libfftw3-3.lib"
fftw文件
在thridarty文件夹下新建一个fftw的文件夹,将.h和.lib文件放进去,(可以把dll文件也放进去然后在运行后让vs帮忙复制),dll文件放到解决方案路径下的平台debug或release文件夹内。(这里因为不会涉及变动,直接放在编译文件夹下就可以了)
在“配置属性”>“链接器”>“常规”
>“附加库目录”中输入../thridarty/fftw
在“输入”>“附加依赖项”中添加libfftw3-3.lib
在头文件和源文件下添加 fft_utils.h 和
fft_utils.cpp
,在fft_utils.h里包含头文件fftw3.h将fft做一个封装
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 #ifndef FFT_UTILS_H #define FFT_UTILS_H #include <vector> #include <complex> #include <mutex> #include <unordered_map> #include <fftw/fftw3.h> class FFTUtils {public : using Complex = std::complex<double >; static std::vector<Complex> fft (const std::vector<double >& input) static std::vector<Complex> fft (const std::vector<Complex>& input) static std::vector<Complex> ifft (const std::vector<Complex>& input, bool normalize = true ) static std::vector<double > magnitude (const std::vector<Complex>& input) static std::vector<double > phase (const std::vector<Complex>& input, double epsilon = 1e-10 ) static void clearCache () private : struct PlanCache { fftw_plan forward_plan = nullptr ; fftw_plan inverse_plan = nullptr ; fftw_complex* in = nullptr ; fftw_complex* out = nullptr ; }; static std::unordered_map<size_t , PlanCache> plan_cache_; static std::mutex mutex_; static PlanCache& getPlanCache (size_t size) static void ensurePlanExists (size_t size) FFTUtils () = delete ; ~FFTUtils () = delete ; FFTUtils (const FFTUtils&) = delete ; FFTUtils& operator =(const FFTUtils&) = delete ; }; #endif
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 #include "fft_utils.h" #include <stdexcept> #include <cmath> #include <algorithm> std::unordered_map<size_t , FFTUtils::PlanCache> FFTUtils::plan_cache_; std::mutex FFTUtils::mutex_; FFTUtils::PlanCache& FFTUtils::getPlanCache (size_t size) { std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock (mutex_) ; ensurePlanExists (size); return plan_cache_[size]; } void FFTUtils::ensurePlanExists (size_t size) if (plan_cache_.find (size) != plan_cache_.end ()) { return ; } PlanCache cache; cache.in = fftw_alloc_complex (size); cache.out = fftw_alloc_complex (size); if (!cache.in || !cache.out) { throw std::bad_alloc (); } cache.forward_plan = fftw_plan_dft_1d ( static_cast <int >(size), cache.in, cache.out, FFTW_FORWARD, FFTW_ESTIMATE ); cache.inverse_plan = fftw_plan_dft_1d ( static_cast <int >(size), cache.in, cache.out, FFTW_BACKWARD, FFTW_ESTIMATE ); if (!cache.forward_plan || !cache.inverse_plan) { fftw_free (cache.in); fftw_free (cache.out); throw std::runtime_error ("无法创建FFT计划" ); } plan_cache_[size] = cache; } std::vector<FFTUtils::Complex> FFTUtils::fft (const std::vector<double >& input) { const size_t size = input.size (); if (size == 0 ) { throw std::invalid_argument ("输入向量不能为空" ); } PlanCache& cache = getPlanCache (size); for (size_t i = 0 ; i < size; ++i) { cache.in[i][0 ] = input[i]; cache.in[i][1 ] = 0.0 ; } fftw_execute (cache.forward_plan); std::vector<Complex> result (size) ; for (size_t i = 0 ; i < size; ++i) { result[i] = Complex (cache.out[i][0 ], cache.out[i][1 ]); } return result; } std::vector<FFTUtils::Complex> FFTUtils::fft (const std::vector<Complex>& input) { const size_t size = input.size (); if (size == 0 ) { throw std::invalid_argument ("输入向量不能为空" ); } PlanCache& cache = getPlanCache (size); for (size_t i = 0 ; i < size; ++i) { cache.in[i][0 ] = input[i].real (); cache.in[i][1 ] = input[i].imag (); } fftw_execute (cache.forward_plan); std::vector<Complex> result (size) ; for (size_t i = 0 ; i < size; ++i) { result[i] = Complex (cache.out[i][0 ], cache.out[i][1 ]); } return result; } std::vector<FFTUtils::Complex> FFTUtils::ifft (const std::vector<Complex>& input, bool normalize) { const size_t size = input.size (); if (size == 0 ) { throw std::invalid_argument ("输入向量不能为空" ); } PlanCache& cache = getPlanCache (size); for (size_t i = 0 ; i < size; ++i) { cache.in[i][0 ] = input[i].real (); cache.in[i][1 ] = input[i].imag (); } fftw_execute (cache.inverse_plan); std::vector<Complex> result (size) ; const double scale = normalize ? 1.0 / size : 1.0 ; for (size_t i = 0 ; i < size; ++i) { result[i] = Complex ( cache.out[i][0 ] * scale, cache.out[i][1 ] * scale ); } return result; } std::vector<double > FFTUtils::magnitude (const std::vector<Complex>& input) { std::vector<double > result (input.size()) ; for (size_t i = 0 ; i < input.size (); ++i) { result[i] = std::abs (input[i]); } return result; } std::vector<double > FFTUtils::phase (const std::vector<Complex>& input, double epsilon) { std::vector<double > result (input.size()) ; for (size_t i = 0 ; i < input.size (); ++i) { result[i] = std::atan2 (input[i].imag (), input[i].real () + epsilon); } return result; } void FFTUtils::clearCache () std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock (mutex_) ; for (auto & entry : plan_cache_) { PlanCache& cache = entry.second; if (cache.forward_plan) { fftw_destroy_plan (cache.forward_plan); } if (cache.inverse_plan) { fftw_destroy_plan (cache.inverse_plan); } if (cache.in) { fftw_free (cache.in); } if (cache.out) { fftw_free (cache.out); } } plan_cache_.clear (); }
加入测试代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 bool test_fft (size_t size, double epsilon) try { std::cout << "===== start FFT test :" << size << " =====" << std::endl; std::vector<double > input (size, 0.0 ) ; for (size_t i = 0 ; i < size / 2 ; ++i) { input[i] = 1.0 ; } std::cout << "before" << std::min (size, (size_t )5 ) << "points: " ; for (size_t i = 0 ; i < std::min (size, (size_t )5 ); ++i) { std::cout << input[i] << " " ; } if (size > 5 ) std::cout << "..." ; std::cout << std::endl; auto fft_result = FFTUtils::fft (input); std::cout << "after FFT" << std::min (size, (size_t )5 ) << "points: " ; for (size_t i = 0 ; i < std::min (size, (size_t )5 ); ++i) { std::cout << "(" << std::fixed << std::setprecision (2 ) << fft_result[i].real () << "," << fft_result[i].imag () << ") " ; } if (size > 5 ) std::cout << "..." ; std::cout << std::endl; } catch (const std::exception& e) { std::cerr << "error: " << e.what () << std::endl; return false ; } }
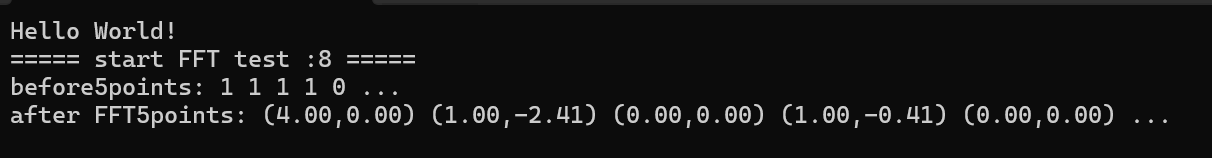
以上fft代码均由豆包生成。生成dll,并在客户端调用这个函数,发现成功运行。
fft调用
参考文档
C++
日志库 Spdlog 报错: “Unicode support requires compiling with
/utf-8“
【C++】spdlog光速入门,C++logger最简单最快的库